If you want to protect your data against prying eyes, the best bet is encrypting your entire hard drive, rather than individual files or folders. Whether on macOS or Windows, a number of useful tools are available, and below, we'll let you know what these are and how to use them.
Unencrypted Data Storage Devices - Easy Prey
If a thief breaks into your apartment and makes off with your laptop, it won't take long before they'll be browsing its contents. It's a common misconception, but password-protected Windows accounts actually only offer a limited amount of security; should a thief remove your hard drive and connect it to another computer, they'll be able to access everything on it no matter how strong your password was.
The same fate can befall external hard drives and USB sticks, should they come into the wrong hands. If you lose your flash drive, for example, whoever finds it gains access to all of the data on it. For this reason, hard drives and mobile storage devices of all shapes and sizes should be encrypted.
How Encryption Algorithms Secure Your Data
Encryption algorithms rely on so-called cryptographic keys, which change plain text into encrypted text. In this manner, data is repackaged as numbers, which are converted back to their original form so long as the correct password is input. Guessing or brute-force won't offer much help in breaking the key since for the default algorithm (AES 256), there are 2^256 possible combinations. Even the most powerful computer would require billions of years to try that many.
Which Devices Are Encrypted by Default?
Unless otherwise notes, all (new) Apple products including Macs and iPhones.
Most (new) smartphones with Android installed.
Encryption for Windows: BitLocker
BitLocker can be used to encrypt an entire drive or partition, relying on the so-called Trusted Platform Module (TPM). This is a chip that comes pre-installed with most new computers and laptops.
Should your entire hard drive by encrypted, Windows will prompt you for the key when booting up. In the event that you lose this password, you can regain access through a recovery key.
BitLocker offers users the choice of the following encryption algorithms, with the number of bits corresponding to the key's length:
AES-CBC 128-bit
AES-CBC 256-bit
XTS-AES 128-bit
XTS-AES 256-bit
To check whether your computer or laptop has a TPM chip, go to the Windows menu and follow Settings > Device Manager > Security Devices. Should a TPM chip be present, it will be listed here as "Trusted Platform Module 2.0".
In the event that your computer or laptop doesn't have a TPM chip, you can still encrypt your hard drive with BitLocker, however, you'll need a USB stick with a startup key to access it.
How to Activate BitLocker
1. Click on Start, type "BitLocker" in the search field, and press enter.
2. A window, Bitlocker Drive Encryption should open (see the screenshot below). Click on Turn On BitLocker for the drive you'd like to encrypt. Starting with Windows 10, it's possible to encrypt only used storage space, saving time. The only downside is that this isn't as secure as encrypting the entire drive.
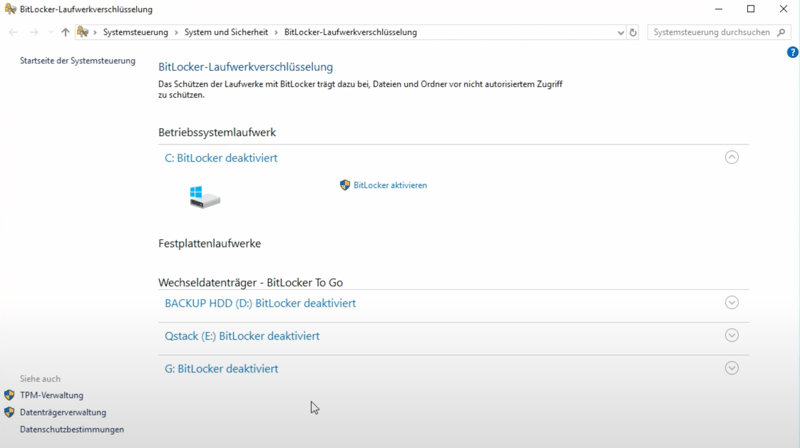
With BitLocker, it's possible to encrypt only used storage space on your drive.
3. Specify where the recovery key should be saved. You can store it in your Microsoft account, print it, or save it to a USB stick. The last option is the safest since it means that the key won't be located remotely, but rather, on your hardware. To err on the side of caution, we also recommend printing out a hard copy of the key.
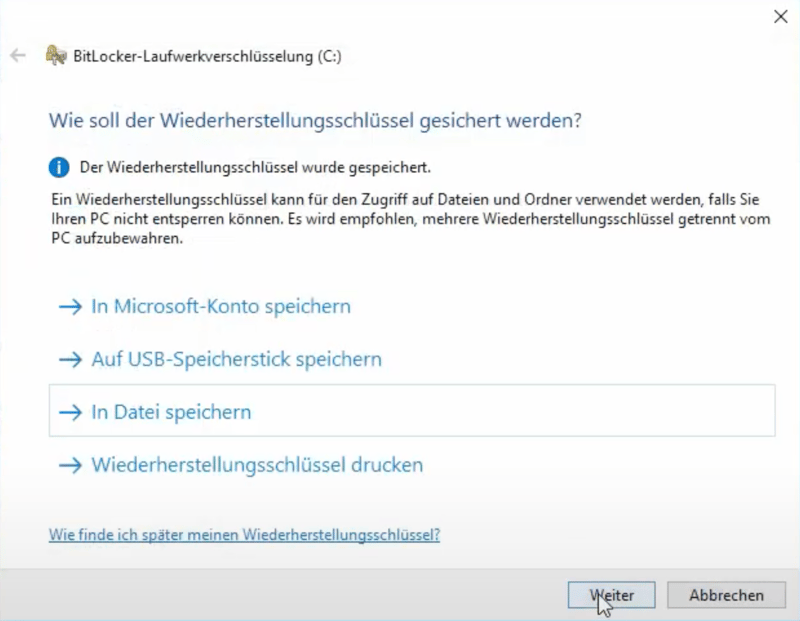
Windows offers a range of different options for storing your recovery key.
4. Select the encryption mode. New is recommended for internal drives, while Compatible is the best option for external devices.
5. Confirm your selection by clicking on Next and BitLocker will encrypt the drives you've specified. You'll know it has completed the process when your computer restarts.
Advantages of using BitLocker
Highly secure
Easy to install and use
Doesn't consume many system resources
Disadvantages of BitLocker
Requires Windows Professional or Enterprise
Should your computer or laptop not have an integrated TPM chip, can only be used with an external USB stick.
Encryption for Macs: FileVault
In contrast to Windows, iMac Pros and other Mac hard drives are encrypted by default with a T2 chip since OS X 10.10 Yosemite (2014). FileVault only allows decryption to commence after the correct password has been input, while also providing a number of additional security features to Mac users.
How FileVault works
FileVault utilizes the XTS-AES-128 encryption algorithm with a 256-bit key. In addition to internal drives, this allows external ones to be encrypted as well.
How to activate FileVault
1. Open the Apple menu and go to System Settings > Security.
2. Click on FileVault.
3. Confirm by clicking on Activate FileVault.
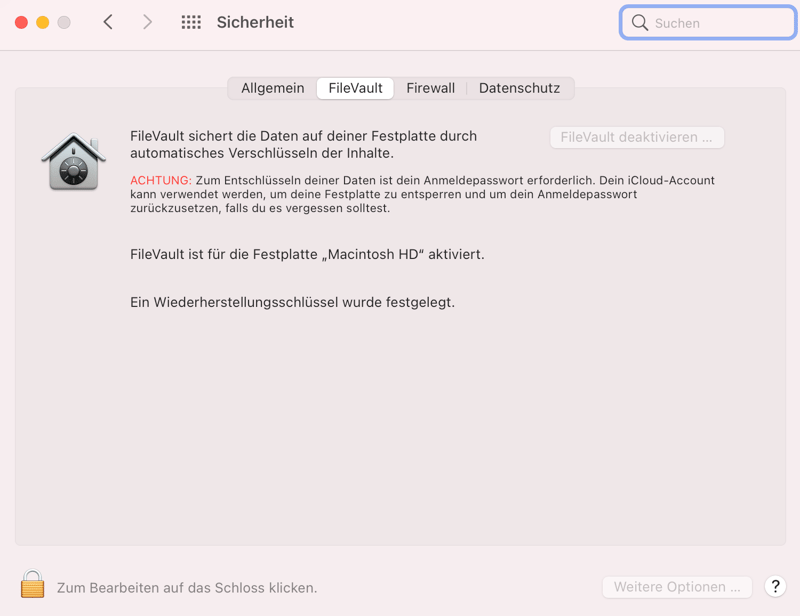
With FileVault macOS users can encrypt sensitive data.
4. Next, select how the drive should be unlocked in the event that you lose the key, either through a recovery key or by accessing your password-protected iCloud account.
Advantages of FileVault
Highly secure
Easy to use
Doesn't significantly impact your computer's performance
Encryption for External Hard Drives: VeraCrypt
VeraCrypt, a piece of open-source software based around the TrueCrypt algorithm, is one of the most well-known third-party encryption programs out there. In 2020, the Fraunhofer Institute confirmed that VeraCrypt's encryption algorithm had no significant weaknesses. Beyond that, the program makes it possible to decrypt data encrypted on Macs on Windows and vice versa.
How VeraCrypt works
The program encrypts internal and external drives, as well as folders using the TrueCrypt algorithm, supporting Windows, Linux, and macOS. Only after the correct password has been input will it display the virtual drives it has encrypted, and even then, it's possible to add hidden drives within the encrypted container, boosting security even further.
How to activate VeraCrypt
1. Download the software, extract its files, and install them on your computer.
2. In order to create a virtual drive, launch the software and click in the bottom left on Create Volume > Encrypt a System Partition or Drive. Select the desired drive.
3. From the three options, choose Create an encrypted file container.
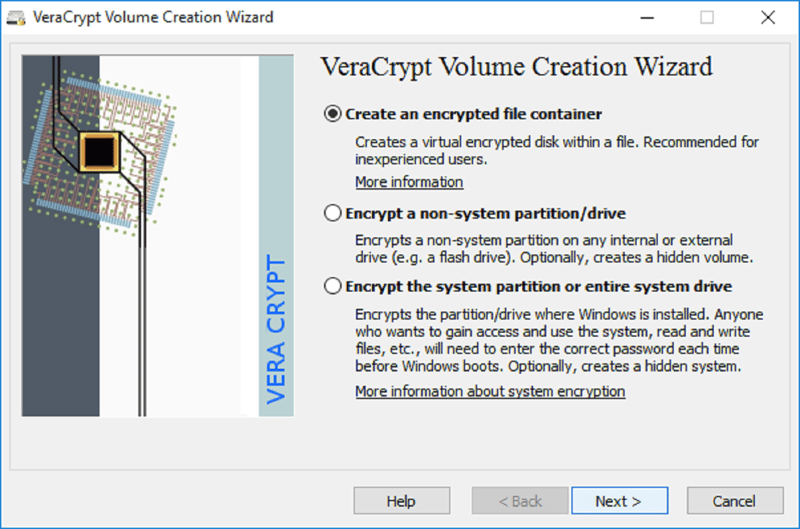
Select Create an encrypted file container.
4. Choose an encryption algorithm. We recommend AES, since it offers both speed and security.
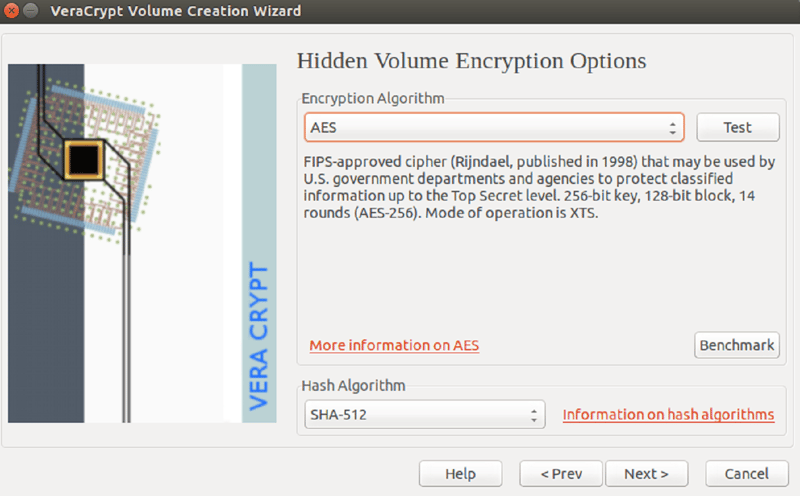
AES has a reputation for being difficult to crack.
5. Once you've confirmed your selection, VeraCrypt will encrypt the drive you've selected and store the files you've specified in the appropriate container, which will appear as an additional drive. Simply disconnect this drive, and the files will be encrypted, requiring a password to be unlocked or accessed again.
Advantages of VeraCrypt
Highly secure
Compatible with multiple operating systems
Free and open-source
Disadvantages of VeraCrypt
Somewhat more difficult to use than BitLocker or FileVault
Conclusion
Encrypting your hard drive is the best way to protect your files from unauthorized access, theft, and loss. With BitLocker, Windows provides a secure and efficient piece of software, however, only for its Professional and Enterprise users. All Mac users can take advantage of FIleVault, that operating system's counterpart to BitLocker. The free option, VeraCrypt, offers a solution compatible with multiple operating systems, but also one which requires a bit more time to get used to.
FAQs
Even though all of the tools we've detailed above rely on different algorithms and processes, encryption occurs in each more or less in the same manner. First, you'll need to select the drive you'd like to encrypt and the encryption algorithm you'd like to use. After that, you'll be prompted to create a secure password and save the recovery code either in the cloud or locally on your system. Then, the drive or folder will be encrypted and you'll be informed that the process has completed.
External data storage devices can be encrypted in the same manner as internal ones, with BitLocker and FileVault supporting both. The same is true of most commercial and open source programs, such as VeraCrypt.
Tools like BitLocker (Windows) and FileVault (macOS) are considered highly secure, however, their encryption only protects inactive drives that are offline. The moment you've decrypted a drive and connected to the Internet, it will be accessible to cybercriminals. The same holds true for decrypted USB sticks and hard drives. For this reason, antivirus programs and firewalls are essential complements to an encrypted drive or disc.
Even the most secure encryption algorithm can be undone if a third-party is capable of easily guessing the password you've created. To make sure that this doesn't happen, your password should:
Be at least 10 characters, or ideally, 16 characters long.
Composed of numbers, upper and lower-case letters, as well as symbols.
Not contain your name, birthday, address, or other personal information.
To help in creating a secure password automatically, feel free to use our complementary password manager.
Should you forget or lose your password, you can unlock the drive with a recovery key. This is a code that contains a collection of numbers (for example, with BitLocker, it's 48 numbers). The best idea is to print this out when encrypting your drive and store it in a safe place, since without it, your hard drive or USB stick will remain locked forever. Alternatively, you can save this code to the cloud.