What Can Someone Do With Your IP Address? (+ 4 Ways to Hide It)
Your IP address is a bit like a passport for your devices. It's a unique identifier that tells websites who you are and where you're from, allowing you to travel through networks and exchange information with other devices. Losing a passport is a big deal, but what about 'losing' your IP address?
Read on to find out why IP addresses are so important, what they're normally used for, and what can happen if they fall into the wrong hands. You'll also learn about ways to hide and change your IP address, if necessary.
What Even Is An IP Address – And What Does It Do?
Every device that's connected to the internet has an Internet Protocol (IP) address. It's a unique identifier that enables communication and data transfer.
It works much like a physical address: just like a house needs an address to receive letters, a computer needs an IP address to send or receive information over the internet. Without these addresses, it would be nearly impossible to track billions of data exchanges happening online.
What does an IP address look like?
Essentially, an IP address is a string of numbers separated by periods (IPv4) or colons (IPv6). The main difference between IPv4 and IPv6 is address size: while IPv4 uses a 32-bit address, IPv6 uses a 128-bit address. Therefore, IPv6 IP addresses are a lot longer – and because IPv6 offers more combinations, there are lots more possibilities for unique IP addresses, solving the issue of IP address exhaustion.
Here are two examples for public IP addresses:
IPv4: 104.26.5.112
IPv6: 3A52:9109:7DC0:6774:7238:7746:DD5F:8B9A
Besides IPv4 and IPv6, there are other ways to classify email addresses, such as “public” vs “private” or “static” vs “dynamic”. Check out our article to learn more about the different types of IP addresses and how they work:
What Your IP Address Reveals About You
It's just a string of digits, but your IP address contains quite a bit of information about you. While it doesn't reveal specific personal details like your name or physical address, it does offer some general information about your online activities and geographical location.
Geographic location
Your IP address can reveal your general geographic location – down to the city or postcode – but not your exact address. That's because internet service providers (ISPs) are allocated blocks of IP addresses for different regions. That's why you get relevant local ads, weather forecasts, and other services tailored to your location.Online activities
Although an IP address doesn't give a detailed account of what you do online, it can paint a broad picture. For instance, websites can keep logs of the IP addresses that visit them. If the same IP address is used to access certain websites repeatedly, it could indicate a pattern of behavior. Hiweverm this doesn't equate to tracking individual browsing history.Information from your ISP
In many countries, Internet Service Providers (ISPs) are legally required to store certain customer data. In the event of criminal activity, authorities can access this stored information to identify the account holder.
As you can see, your IP address can reveal some information about you. How about a demonstration? Our Browser Privacy Check reveals which traces you or your browser leave on the web, partly through your IP address.
Of course, this kind of tracking isn't always a bad thing. It can improve the user experience on certain websites, provide you with more relevant ads and search results, and it's generally just part of going online. That's why many people don't mind a bit of IP-snooping from legitimate businesses.
But besides general privacy concerns, there is always the possibility that your IP address lands in the hands of someone who's up to no good. The question is: what can anyone even do with it?
What Can Someone Do With Your IP Address?
That really depends on who we're talking about here. After all, there are plenty of perfectly legitimate entities who can use your IP address for all sorts of purposes, some of which you might find objectionable. On top of that, there are malicious actors who might use your IP address to attack or exploit you.
Let's look at both:
Your IP Address In The Hands Of Corporations & Governments
It's not just cybercriminals who take an interest in our IP addresses. Governments and corporations find a lot of use for our digital identifiers – for better or worse. Here are some examples:
Surveillance and crime fighting
Governments around the world use IP addresses to fight crime and maintain national security. Tracking down IP addresses can help law enforcement to solve crimes and discover illegal behavior. But where some see law and order, others see concerns about privacy and government surveillance. In extreme cases, IP addresses can be tools for censorship or unjust punishment. A lack of digital privacy can also have a chilling effect on freedom of speech.Geoblocking
Companies and governments can use your geographic location to decide which content you can and cannot access. Geoblocking is the practice of restricting digital content based on where users are connecting from. Because an IP address contains location data, it helps the servers of websites determine who gets access.There are many legitimate reasons for geoblocking. Streaming services such as Netflix or Amazon Prime Video enter licensing agreements for each country they operate in, which dictate precisely which content they can show where. This leads to discrepancies in content availability across different regions, which can be annoying for customers (to bypass these restrictions, you can use a VPN – more on that later).
Once again, oppressive regimes can use geoblocking for more sinister means: as a form of digital censorship, restricting access to critical news sites, social media platforms, or any content deemed unsuitable by the government.
Targeted Ads
IP addresses are useful for advertisers, too. By tracking your general location, they can show you localized ads or offers.Location-based pricing
It's not just streaming content that depends on a user's location: online retailers might present you with different prices for the same product or service depending on where you are.Cross-Website User Profiles
Tech companies can use IP data to create user profiles that span across multiple websites.
Governments and corporations are one thing – but what can hackers and scammers do with your IP address? Let's take a look:
Your IP Address In The Hands Of Hackers & Scammers
First of all, relax: even in the hands of the ill-intentioned, your IP address alone usually isn't enough to cause substantial damage. If someone is specifically targeting you, however, your IP address can be exploited as part of broader cyberattacks.
By getting hold of your IP address, a malicious actor could:
Uncover your geographical location
Your IP address can reveal your approximate geographical location, down to the city level or even your neighborhood. While this information isn't precise, it can still be used to make educated guesses about other aspects of your life. Cybercriminals might use your location data for phishing scams, for example, disguising their deceptive communications as local services you may use.Launch DDoS attacks
In a Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack, which can be launched with someone's IP address, hackers try to overload your network with unwanted data or requests, causing your internet connection to slow down or even disconnect entirely. This is annoying for individual users – but it can be a real source of trouble for businesses.Try to hack you
A skilled hacker might be able to use your IP address for any number of exploits. Port scanning a known IP address – basically knocking on doors to find open ports and devices – is a common starting point for hackers, for example.Commit identity thefts and scams
While your IP address itself doesn't contain any personal information, it can be used alongside other data in certain scams or deceptive practices. For example, someone could use your IP address to send you emails that appear to be from your ISP, tricking you into revealing sensitive information.
The potential misuse of your IP address may sound frightening, but it's important to remember that having someone's IP address alone does not open a straightforward pathway to severe harm.
Most online platforms have robust security measures to prevent such attacks. Below, we'll explore various ways to further safeguard your IP address and, by extension, your online presence.
How To Protect Your IP Address
You can't keep your IP address a secret – and you shouldn't have to. Without IP addresses, the internet would collapse, they're a fundamental building block of the digital world. You don't always have to share it with everyone, however, and there are ways to hide and protect your IP address from certain actors, be it governments, corporations, or hackers.
Precautionary measures
Keeping your IP address secure isn't necessarily about hiding or changing it, but ensuring that it's only accessible when absolutely necessary. Here are some precautionary measures:
Keep your software and OS updated: Cybercriminals often use outdated software as a loophole into your system, and uncovering your IP address can be part of that. By ensuring your apps and systems are up-to-date, you fortify your defenses.
Be careful with unsolicited emails and suspicious links: Hackers might try to get your IP address through phishing emails or malicious links. Stay vigilant and don't click on anything you don't trust.
Avoid public Wi-Fi or use with caution: Your IP address and your privacy in general are more vulnerable in public networks. If you do need to use them, you might want to use protective tools like VPNs.
Use a firewall or antivirus program: Active and updated firewalls are your first line of defense, detecting and warding off most unauthorized access attempts. Antivirus software might add another layer of protection, safeguarding against malware that might attempt to expose or misuse your IP.
Changing your IP address
There are also ways to actively change your IP address – not just for protection, but also to bypass restriction like geoblocking. Here are your main options:
Get a new IP assigned from your ISP
Depending on what type of IP address you're assigned, changing it might be as simple as restarting your router. Here's where the difference between dynamic and static IPs comes into play:
Dynamic IPs: If you're using one of your home devices, such as your personal smartphone or desktop PC, you've probably received a dynamic IP address from your ISP. That means your IP address changes periodically anyway, and you might obtain a new IP simply by restarting your router. You can also manually change your IP on the device you're using.
Static IPs: In business infrastructures, static IPs are more common. These don't change unless specifically requested from the ISP. If you believe there's a valid reason for an IP change, your ISP might assist.
Use a VPN
You can think of a VPN as a kind of tunnel between your device and the website you're trying to visit. As an intermediary, it diverts your traffic via its own servers, changing your IP address in the process. That way, the websites you're visiting don't see your IP address, but that of the VPN server.
By connecting to servers in specific countries, you can use this VPN tunnel to bypass geo-restrictions and access specific content on streaming servers, or to evade government censorship, such as China's Great Firewall.
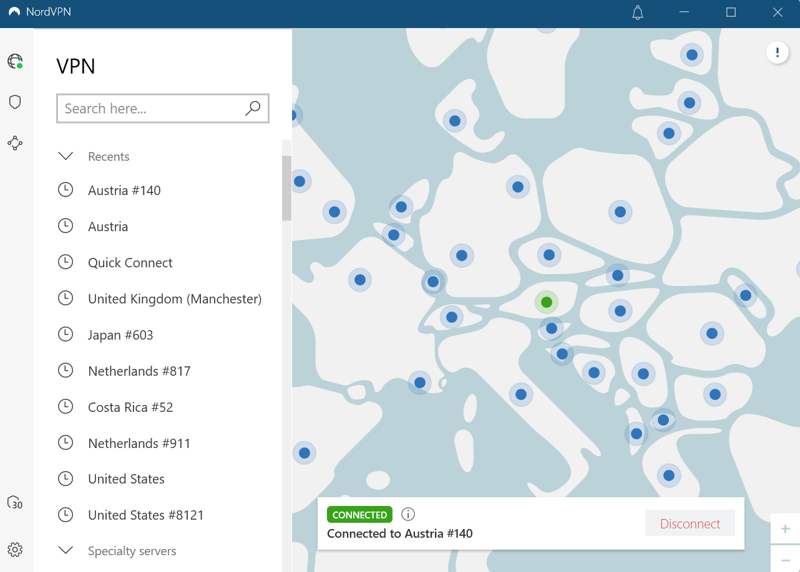
With a VPN service like NordVPN, you can connect to servers all over the world.
Be aware that VPNs don't ensure perfect privacy either. Instead, they just add another layer to your connection – and instead of the websites you're visiting, your IP address is now visible to your VPN provider. That's why you should only use reputable VPN services. You can use our reviews and comparisons to find the best provider for your needs:
Use a proxy
Similar to VPNs, proxies act as intermediaries between your devices and the internet. Each request is processed via the proxy server, hiding your original IP address. In contrast to VPNs, however, proxies don't generally encrypt your data, which makes them less secure overall.
Use Tor
Tor is a secure browser that reroutes your traffic through several servers. When you visit websites via Tor, it's extremely challenging for anyone to trace back to your original IP address. The downside of this security mechanism? The Tor browser tends to be quite a bit slower than regular browsers.
Conclusion
What can someone do with your IP address? Turns out, quite a bit – and that's not usually a bad thing. IP addresses are a fundamental building block of the internet and play an instrumental role in ensuring seamless communication between devices across the globe.
But like any tool, IP addresses can be used for beneficial and malicious purposes. Governments can use them to fight crime, or to spy on their citizens. Companies can use them to streamline their services, or to invade your privacy and keep building their data empires. Cybercriminals may use them to hack or scam you.
In the end, you can't keep your IP address a secret, and even in the wrong hands, an exposed IP address alone usually not enough to do real damage. As long as you take basic online precautions, you should be reasonably safe. And if you need to hide or change your IP for specific purposes, for example to evade geoblocking, you can use tools like VPNs.
Frequently Asked Questions
No, you shouldn't be worried if someone has your IP address. An IP address can be used as an entry point by really skilled hackers targeting you specifically, but it's usually not enough to get you into real trouble. Besides, there are lots of actors online who need your IP address to provide basic services or streamline their offering.
Depending on the device you're using, you can find your IP address with just a few clicks or taps. On a Windows device, for example, just open the Command Prompt, type ipconfig, and look for the IP address section. You can also use web tools, such as Whatismyipaddress.com.
There are many ways to change your IP address. If you're using a dynamic IP, it might be enough to just restart your router to have your ISP allocate a new IP address. If you want to get an IP address from a specific country, for example to bypass georestrictions, you can use services like VPNs or proxy servers.