The meeting room is silent, and everyone sits with their heads down or stares off into space - nobody has a solution to the problem. If only the group could brainstorm innovative solutions and get around the roadblock. Ideas would flow freely among the team, and participants could pick the best option for further study and implementation.
There are many different ways to encourage brainstorming and in this article, we'll take a look at some of the most popular to help you choose the best option for your organization. Near the end, we'll also offer some tips about how to get the most out of your team's next brainstorming session.
What Is Brainstorming?
Brainstorming is a technique that helps to come up with new ideas. Even though some of the approaches below can be used by individuals, most are intended for groups. Whenever a team faces a problem or wants to further a product's development, brainstorming can help identify the right solution.
The term was first introduced in 1939 by Alex Osborn. He wanted to promote creative environments where ideas could flow freely. For inspiration, he oriented himself on the English translation of an Indian manta "using the brain to storm a problem".
To actually create an environment that encourages new and innovative ideas, and where brainstorming is possible, you'll need to take note of a few rules.
Rules
There are four golden rules of brainstorming. Failure to follow these will prevent you from unlocking the full creative power of your team and their ideas. They are:
No judgements
Participants don't judge each other or their ideas. This includes both verbal and non-verbal forms of criticism and even evaluation of a proposal's merits. Is an idea good or bad? You'll never know during a proper brainstorming session. While this might sound difficult, it makes participants much more comfortable and creative.Encourage diverse ideas
During a brainstorming session, the goal is to generate as many ideas as possible. Unlike most things in business, it's less about quality than quantity. This cannot be emphasized enough, as any limitations inhibit creativity.Innovate ideas further
Any idea that's expressed can be addressed, added to, or modified. Often, one suggestion or comment will inspire another team member, who develops the original idea further. The process repeats, with newer, more refined ideas and approaches the result.Go wild!
There's no idea that's too far-out, unrealistic, or unorthodox for a brainstorming session. Don't hesitate to approach challenges from a completely different perspective and offer an unconventional solution. The weirder, the better, since this helps creative juices flow. And who knows, you might stumble upon a solution that was never considered before.
When a team follows these rules, real creativity can be unleashed.
Process
Brainstorming can be divided into two phases:
Phase 1: Gather ideas
In this phase, the team focuses on the generation and collection of new ideas.
Phase 2: Evaluation
Next, the team jointly reviews the results of the first phase. This is when individual ideas are discussed, sorted, and evaluated. Once finished, the team should have a handful of promising leads for things that they can try out.
It's recommended to limit the amount of time allocated to both phases so that the process doesn't get out of hand. Specify the amount of time that your team will brainstorm before you start the session. After you've wrapped up the second phase, you'll either have a list of ideas or one in particular that you'd like to pursue further.
The rules and phases mentioned above apply regardless of the brainstorming technique you use. Make sure that the team is aware of them before you start the brainstorming session.
5 Brainstorming Techniques: An Overview
Since more and more businesses rely on brainstorming, it comes as little surprise that the number of brainstorming techniques is constantly growing. Below, we'll introduce you to five popular techniques that can be applied to a wide range of different problems and situations.
Mind Mapping
Mind mapping (or creating a mind map) is an excellent way to gather new ideas since it encourages creativity and visualizes thought processes. The team writes down a key subject or element in the middle of a piece of paper or on a whiteboard. Then, everyone takes turns adding different related aspects. This should form branches and help generate new ideas.
Through visualization of the issue at hand, participants get an excellent overview of a complex topic and can link elements or aspects to one another.
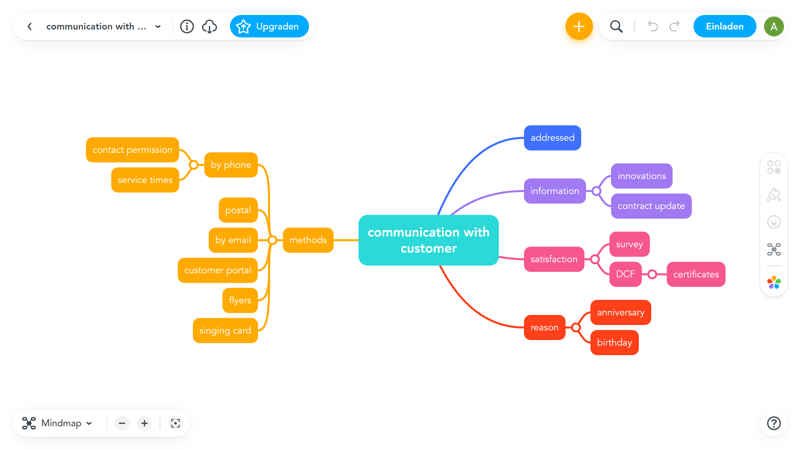
A finished mind map might look like this (created with mindmeister).
This method can be used on its own or within a team, and either digitally or in person.
Brainwriting
For this technique, every participant writes down up to three ideas on a piece of paper or in a document. Once finished, each person gives their three ideas to the next team member, who adds their own ideas, and so on. Everyone who receives a list of ideas attaches their own, along with comments, to the existing ones. Based on how large the team is, this can generate a wealth of new ideas and recommendations.
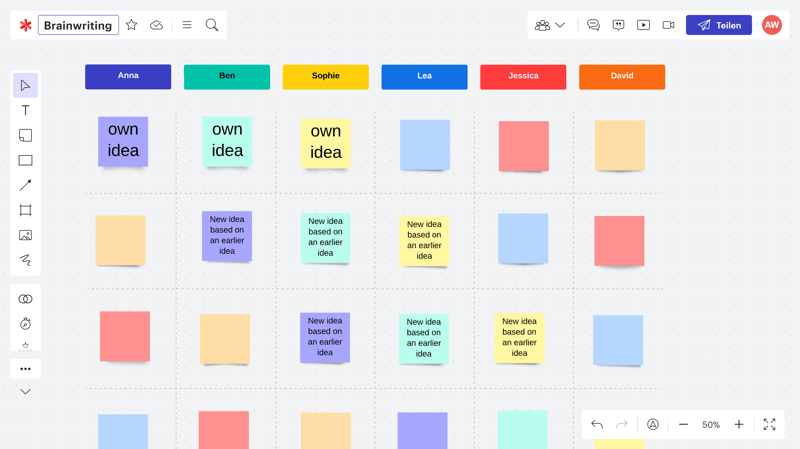
A brainwriting template made with lucid.app.
Brainwriting is highly effective since team members can freely express their thoughts, without any external influence. Because the ideas aren't discussed, no one tries to push their own suggestions or agenda through. Instead, the entire focus is on the generation of new ideas and the further development of existing ones.
Starbursting
Starbursting is a (follow-up) brainstorming technique since it builds and develops an already evaluated idea further. Like a mind map, a starburst also has a single idea at its center, however, the approach is more structured. The star's six points represent various questions that the team should answer: Who, what, when, where, how, and why?
Questions can be formed in a variety of different ways, such as for "Where?":
Where is our target group?
Where do we want to present our product?
Where do we want to install our system?
Where will we get the necessary resources from?
This method can be used equally well by both individuals and groups.
Six Thinking Hats
This approach was introduced to the world by Edward de Bono. His technique sees participants assigned a particular role (a certain hat), which they need to "wear" for the entire meeting. Every hat corresponds to a different perspective on the challenge, problem, or idea.
Edward de Bono distinguished between the following hats:
Facts and information (white hat)
Feelings and emotions (red hat)
Negative: Plus, Minus, Interesting (black hat)
Positive: PMI (yellow hat)
New ideas, creative thinking (green hat)
The big picture, managing (blue hat)
It's also possible to create other thinking hats for brainstorming, based on which factors and perspectives are important to your team and organization.
Example: If the effects of an idea are particularly important, participants might be given a corresponding hat, while in another situation, the customer's thinking could be turned into a hat. Over the course of the meeting, participants can only evaluate according to the perspective of the hat they're wearing. This ensures that the team views the idea from a range of different perspectives.
The Stepladder
When it comes to brainstorming, the Stepladder techniques takes a bit more time than the others. Its main advantage is that it helps more introverted participants voice their opinions and keeps those of more extroverted team members in check. Here's how it works:
- 1.
The subject of the brainstorming session is introduced.
- 2.
Everyone leaves the room except for two participants. Those outside can already start to discuss ideas, however, they cannot share them with one another. The two participants in the room are allowed to share and discuss ideas, however.
- 3.
Another team member enters the room and introduces his or her idea. Only after that will the original two participants share their ideas and thoughts.
- 4.
This process is repeated until everyone is in the room and all ideas have been jointly evaluated.
The Stepladder technique also works with larger groups. To make sure that brainstorming happens as smoothly as possible, it's good to follow several, agreed-upon guidelines.
Brainstorming Tips
We've prepared a number of tips below that will help your next brainstorming session to be as open and creative as possible.
Choose a Skilled Moderator
Many techniques, such as the Stepladder, require an attentive moderator. This is a key role since moderators ensure that both brainstorming phases occur separately from one another and that the four rules of brainstorming are observed.
A moderator can also act as the session's timekeeper and keep the team aware of how much time they have to discuss whatever topic they're on. They should also be familiar with and experienced with different brainstorming techniques. In this way, they can react if the creative process goes off the track or gets bogged down.
Well-prepared moderators organize the brainstorming session, gently guide it, and document its results and findings.
Give Creativity a Chance
Creativity takes time. When you first pose a question, don't expect an immediate response. Moderators who do are often met with blank stares and shrugs. Try instead to give the team a few minutes to mull over the question you've asked and to prepare their responses.
It's even better if team members are told what the topic(s) of discussion will be when they're first invited to the brainstorming session.
Create the Right Atmosphere
Build an atmosphere of respect where everyone is willing and feels free to voice their opinions without fear of judgment. The rules above are a good place to start, however, you'll still want to encourage the team to actively foster this kind of environment.
One great idea is to hold your brainstorming sessions out of the office, in a completely different space that's conducive to creativity. As an example, you could rent a co-working space for an afternoon. There, you can write on the walls or put up lots of colorful Post-its with different ideas to let creative juices flow.
If you already have a creative space in your office, that's fine too. Just make sure to use it properly.
Promote Variety
When it comes to variety, there are three dimensions that are important to brainstorming:
First, when you select a brainstorming method, try to pick something that the team hasn't been exposed to before. When you do the same thing over and over again, creativity becomes restricted. Instead, try out different methods and alternate between them, especially if they're used with the same team. Not only will those prevent monotony and boredom, but also, help to break out of old thought patterns.
Variety also relates to the team's composition. When the same people have a brainstorming session every week at a certain time, creativity will definitely decline. Mix up the teams and invite new faces. This will bring fresh air and new impulses and help unconventional ideas to percolate.
Finally, variety in brainstorming means openness to new ways of doing things. You can play music during a brainstorming session, kick things off with an icebreaker, or play a game to get the ball rolling. Whatever you decide on, there are many ways to get overcome mental blocks and promote creativity at work.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Brainstorming
Brainstorming is versatile and can help your team come up with all sorts of new ideas. All the same, this creative technique has both advantages and disadvantages:
Brainstorming Advantages
Generate multiple good ideas at once or further refine existing ones
Promotes creative thinking and helps break through mental blocks
Encourages teamwork
Fast and effective problem-solving method
Techniques are easy to implement
Methods with visualizations help to structure thoughts
View issues from different perspectives
Overcome seemingly impossible challenges or problems
Potential Disadvantages of Brainstorming
Participants might be unable to focus on actual brainstorming, if they're too focused on certain details (anchoring)
Introverts might not flourish in group processes
Too many ideas can cause chaos of exhaustion
Must be overseen by a talented moderator to be effective
Conflict can arise when competing opinions are voiced
Lots of suggested ideas are neither viable or usable
Brainstorming's disadvantages make it clear that the process needs expert guidance and direction. With a skilled moderator and use of the right methods, these can be significantly, if not entirely, reduced.
Brainstorming Tools
Whiteboards and conference rooms are useful, however, not an absolute must for effective brainstorming. There are some tools that allow brainstorming to happen digitally. The biggest advantage of this approach is that all notes and ideas are documented and stored online, which makes them accessible to any participants or stakeholders later on.
Brainstorming tools are very popular, and plenty can be found online (depending on your method). Some of the best include:
However, you don't need dedicated tools to brainstorm: Sometimes, a OneNote notebook will be enough to keep track of ideas.
Conclusion
Brainstorming is a creative technique that uses different methods to ensure that mental blocks can be overcome and that ideas can flow freely. It encourages teams to view issues from different perspectives and to work towards a mutually agreeable solution.
There are nearly endless brainstorming techniques, each of which unlocks creative energy in a different way. Some of the most popular include mind mapping, brainwriting, and starbursting. To ensure that your idea gathering doesn't end in chaos, a moderator must direct the process and keep everyone on the same page. So long as the guidelines are followed, nothing can prevent creativity from taking hold.