Kanban vs. Scrum: A Look at the Differences and Similarities
Agile project management helps businesses to quickly react to new challenges. Two popular iterative methods are Kanban and Scrum. Each breaks down complex projects into smaller, shorter phases and parts that are completed during sprints. This approach allows for difficult and dynamic challenges to be flexibly overcome.
In this article, we'll briefly introduce you to the most important characteristics of both methods and showcase their similarities and differences.
Kanban: Visualize Tasks
Toyota developed Kanban to improve its work and production processes. The agile approach is all about the visualization of tasks and assignments, which, as they near completion, are moved from one Kanban board column to another. These columns are:
Open (To-Do)
In Progress
Done
Additional categories can be included or adapted to meet your project's needs. Their purpose is to show how an assignment moves from the planning stage to completion. Team members include all tasks on the board and move them from left to right. In this way, each participant can see the status of any assignment, as well as what sort of workload teams and even individual members have.
A work in progress, or WIP limit is important for the "In Progress" column. It prevents the team from exceeding its capacities. Until this limit is reached, team members can "pull" new assignments. When a task is pulled, the team member signals that they are able to devote their time and energy to it and that it doesn't need to be completed by someone else.
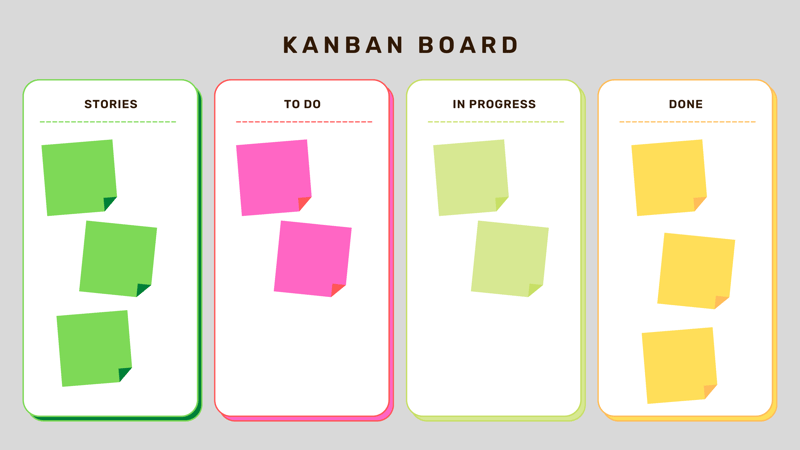
On a Kanban board, assignments move from left to right through different columns.
This method is clear, flexible, and easy to implement. In addition, it transparently displays processes and visualizes work. Since there are no rules in regard to structure, deadlines, or roles, organizations have considerable freedom when they design and implement a Kanban board. Since the goal is continuous improvement and process optimization, coordination is frequent and necessary.
Scrum teams can also use the Kanban method to visualize their efforts.
Scrum: Sprint to Success
Scrum can be traced to software development. The basic idea is that the product under development will never be entirely complete or finished. Instead, versions and iterations (incremental steps toward a solution) are completed in each development cycle (sprint). The agile project management method's framework involves fixed processes, meetings, and cycles, as well as pre-defined roles and tasks/assignments
A sprint doesn't last longer than four weeks. The team works independently and decides ahead of time which tasks will be completed when the sprint finishes. These goals can be visualized on a board. New assignments or tasks cannot be added to an ongoing sprint. Every sprint includes a Daily Scrum, a brief meeting where progress and challenges are discussed.
When a sprint finishes, the team reflects on what was achieved and how teamwork might be improved during the Sprint Retrospective. The next sprint starts immediately thereafter with new goals and improved processes. Scrum events have a fixed structure and standardize the entire approach.
This makes Scrum particularly useful for giving creative processes a framework.
6 Similarities Between Kanban and Scrum
Since both Scrum and Kanban are used in agile project management, there are many similarities between them:
When Kanban is used not only for visualization, it is similar to Scrum in terms of self-organization and coordination (frequent communication).
Team members pull tasks and assignments.
Both frameworks have work-in-progress (WIP) limits: In Kanban, this relates to the maximum number of tasks in the "In Progress" column, while with Scrum, it's more indirect and visible in assignment scheduling during Sprint Planning. A WIP limit ensures that a team isn't overwhelmed by too many assignments. Once a limit has been reached, the team cannot take on any additional tasks.
Both seek to optimize processes and boost efficiency through greater transparency.
In addition to being agile, both Kanban and Scrum are lean. This means that they create value, reduce waste, and eliminate duplication of effort. Different principles and techniques are used to make processes more streamlined and to utilize resources in the most effective way possible. Agility refers to the ability to flexibly and quickly react and adapt to new product requirements.
Both approaches seek to optimize the release plan and reach a final or intermediate result faster. In Scrum, this is measured by team velocity, while for Kanban, emphasis is on the lead time. Velocity indicates the team's working speed and is determined by the average amount of work that a team completes in a sprint.
Lead time, on the other hand, reflects how much time elapses between the customer's request and its delivery or deployment. For this reason, it's sometimes referred to as the delivery time. In Scrum, teams try to reach higher velocities, whereas in Kanban, the goal is to reduce lead time.
6 Differences Between Kanban and Scrum
Despite their similarities, Scrum and Kanban have different applications. In particular, you should pay attention to the following:
Scrum is a more comprehensive framework with specific implementation guidelines, events, and roles. Kanban, on the other hand, offers more creative and design freedom.
In Scrum, the focus is on delivery of a complete "Increment"; with Kanban, workflow processes should be optimized.
Scrum is ideal for complex subjects and topics, however, Kanban is better suited for smaller and more routine tasks. As the number or complexity of assignments increases, oversight can be lost in Kanban.
Kanban is for both individuals and teams, while Scrum is only for the latter.
A team needs to evaluate an assignment before it's scheduled for "The Sprint". With Kanban, assessment is optional.
Teams cannot take on new tasks during a sprint. In contrast, Kanban users can pull a new assignment as soon as they're able to handle it.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Both Methods
Now that you know what their similarities and differences are, it's possible to explore the advantages and disadvantages of each. We'll explore these in the following section.
Kanban's Advantages and Disadvantages
Since the process is flexible, new requirements can be integrated at anytime
Highly transparent, especially for external stakeholders
Team workload is visible
Easier and more understandable process
Focus on the tasks at hand
Lack of a time element can cause deadline or delivery issues
Loses clarity as team size increases
No long-term planning
Scrum's Advantages and Disadvantages
High degree of self-organization
Makes processes transparent
Fixed roles and events provide a roadmap
Project or partial results are available on time
Short planning cycles provide greater flexibility
Significant coordination/communication required
Training required before implementation
New requirements cannot be directly integrated
Kanban or Scrum: Which to Use?
Kanban and Scrum have both advantages and disadvantages. So, how can you decide between the two frameworks? There isn't a single answer, as your choice can depend on a whole range of factors.
One of these is what kind of project you're working on. To help, use the Stacey Matrix: This helps determine the proper management actions for a complex system. A project's requirements (clearly defined or unknown) are plotted on the y-axis, while the x-axis reflects various solutions (known or unknown). Based on their position, projects are said to be simple, complicated, complex, or chaotic.
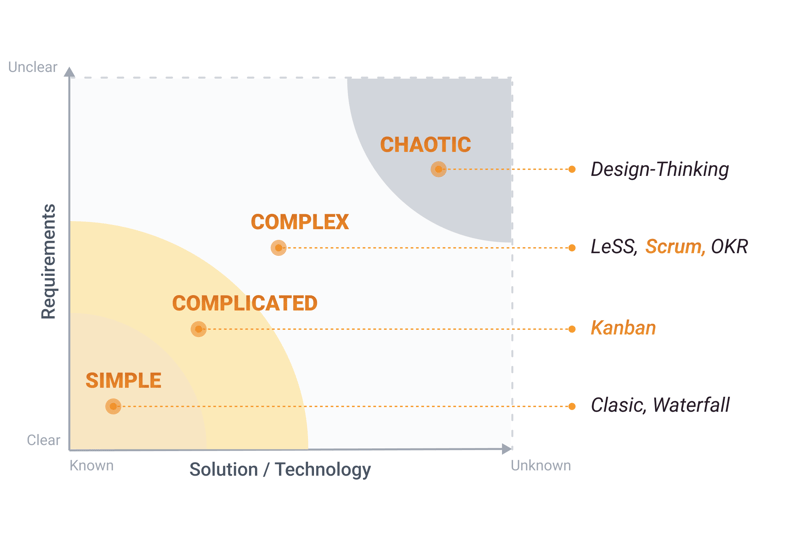
A Stacey Matrix can help you choose the right management method for your project.
The less known your requirements are, and the less familiar you are with the possible solution, the more agile your project will be. Kanban is shown to be ideal for complicated projects, while Scrum is better for complex ones. But why is that?
There are often multiple solutions for complicated projects, however, the cause-effect relationships can usually be easily understood. Complicated projects are often easier than complex ones since their effects aren't as clear. In addition, these may have different objectives.
Before you decide, think about which of these categories you would assign your project to.
Scrumban: The Best of Both Worlds?
Is it too hard to decide between the two methods? Would you prefer to have the advantages of each? You can, with Scrumban. This combines aspects of both Scrum and Kanban. Due to their overlap, Scrumban has the following characteristics:
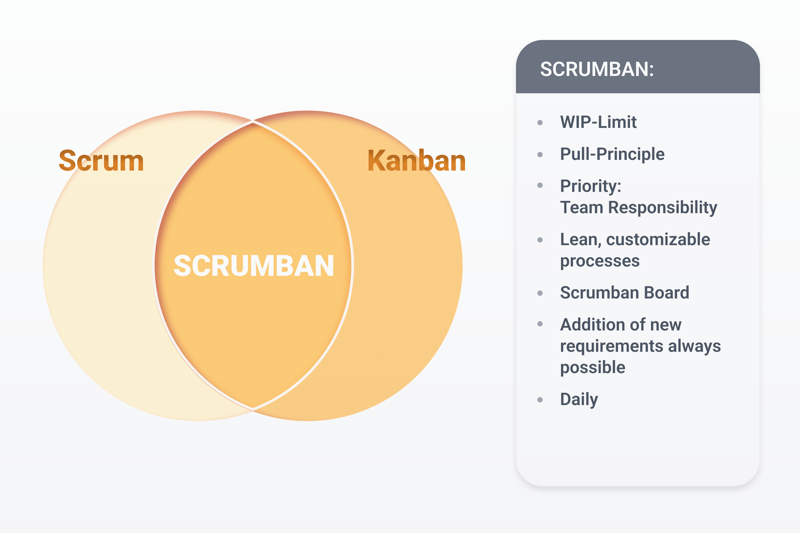
Scrumban combines aspects of Scrum and Kanban.
This approach is particularly useful if you want Kanban's flexibility and Scrum's structure. It's ideal for long-term projects as well as product lifecycles. The biggest advantage of this hybrid approach is that it can be used for a variety of different projects (complicated and complex) and its structure is easy to adjust to your needs.
Conclusion
Kanban and Scrum are the two most well-known agile project management methods. Both share similarities, such as the division of larger projects into numerous, smaller tasks and phases that help teams reach their goals faster and more flexibly.
Whether a project is well-suited for an agile management method and which of the two is better depends entirely on its goal(s) and conditions. Scrum is better overall for complex projects with unknown variables, whereas Kanban is ideal for projects with clearly defined cause-effect relationships.
Frequently Asked Questions
Agile project management offers a way to quickly adapt to changing requirements in the world of project management. Businesses today cannot afford to dedicate years to product development only to realize at completion that the customer has completely different requirements. Agility helps businesses react quickly to changes and integrate them into products through short planning cycles.
Yes, Kanban is an agile project management method. Unlike classic project management, teams can quickly react and adapt to new requirements. The aim: Continuous process improvement.
Whereas Kanban focuses on the visualization of a process, Scrum provides a framework, clear rules, structure, and roles for project work. Scrum is also only intended for teams, while Kanban can be used by both teams and individuals.
This depends entirely on what type of project you're working on. Kanban is recommended for complex projects, however, as size and difficulty increase, Scrum is preferred. There are also other factors you should pay attention to.
Scrumban is a combination of Scrum and Kanban. It's primarily noted for its flexible and adjustable structure which offers the advantages of both approaches in a single model. Be sure to check out our EXPERTE.com guide for more information on Scrumban.