Process Modeling: How to Visualize Business Processes?
Businesses that want to remain competitive need good processes. Many companies have recognized this and use a variety of different tools and measures to optimize their processes. One of them is process modeling.
This approach can help to more clearly define your business's processes. But how does it work, what are its advantages and disadvantages, and which methods and software are there?
In this article, we'll answer all of those questions and more.
Definition
Process modeling visualizes business processes and workflows. If you're wondering what business processes are, there are many different definitions, but here's the one that we like:
"A business process is an activity or set of successive activities that created added value for customers or clients.“
This definition emphasizes the importance of customer relations, however, businesses also use process modeling to visualize internal workflows that don't directly impact clients.
Whatever the case, process modeling is highly versatile and can help businesses gain more insight into all of their activities.
Process Model
Business processes are visualized in a process model. This typically includes several symbols that indicate different business activities, such as reading an email, contributing to a document, or performing a search.
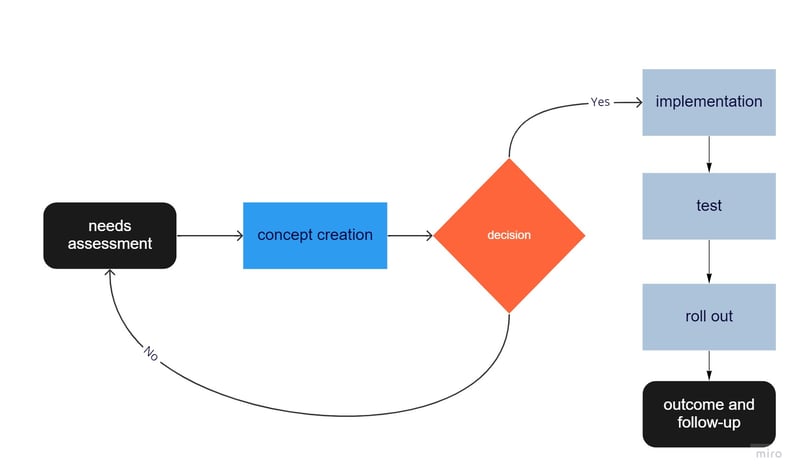
A simplified process visualization is depicted here as a flow chart made with Miro.
Process models can also include consequences and loops that make it possible to adjust a process to different situations or scenarios. These models are important for designing and optimizing business processes.
Sequence of a Business Process - Example
A business process is usually a series of activities that a business conducts to achieve a specific goal. These can either be internal or external and occur physically or digitally.
The sequence of a typical business process might look like this:
- 1.
The process's first activity usually involves identifying a particular need or opportunity. This might be informed through customer feedback, market research, or other insights.
- 2.
Next, a concept is developed to address this need or capitalize upon the opportunities. Brainstorming, prototyping, or other methods are common during this step.
- 3.
Once a concept has been developed, it will be tested and assessed. Customers might be invited to try out the product, or beta testing could be opened.
- 4.
The last stage is process implementation and rollout. To achieve this, lessons, communication, and other activities might be used.
- 5.
The established process is monitored and continually improved, such as through measurements and benchmarking.
The individual steps depend entirely on the business and can vary significantly. However, how does a process result from the five steps above? Let's find out.
Process Modeling Methods
There are many different process modeling methods, however, we're going to introduce you to three of the most popular:
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN)
Business Process Model and Notation is commonly used to visualize business processes. It was originally developed by the Object Management Group (OMG) and has become an ISO standard.
The method is highly flexible and can be adjusted for use with straightforward and complex processes, as well as existing or new processes.
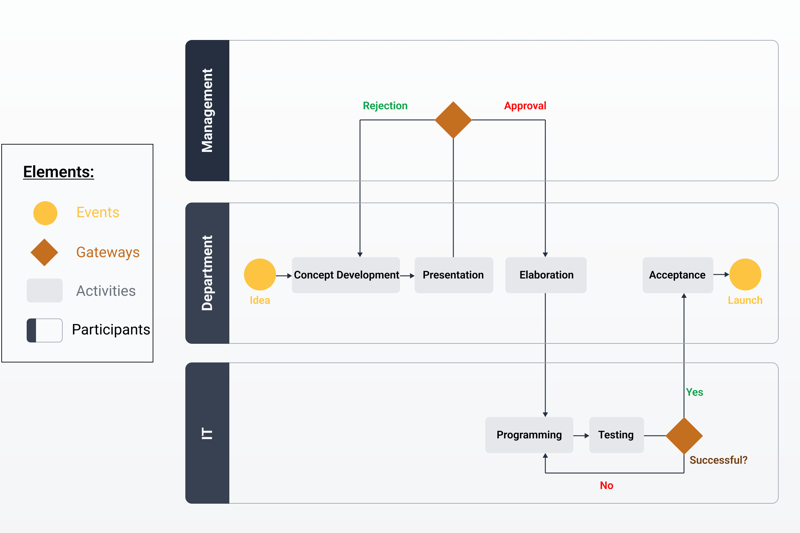
The first step when creating a BPMN is to identify which activities occur within the process. These are then shown in an activity diagram, which is a flow chart that indicates what order the activities occur in as well as dependencies.
A BPMN activity diagram will include Gateways and Events. Gateways are points at which decisions are made that impact whether the process continues or is stopped and depend on the fulfillment of certain criteria.
Events are things that can occur during the process, such as a mistake or timeout.
Once the activity diagram has been created, you can include additional information to more accurately describe the process. This might relate to the process itself, or its various roles, responsibilities, and stakeholders.
BMPN is a powerful tool that can help to accurately describe a process and optimize its efficiency. For these reasons, it's become one of the most popular and commonly used process modeling methods.
UML (Unified Modeling Language)
Unified Modeling Language (UML) is another popular process modeling and visualization method. Many organizations and businesses around the world use UML to create diagrams.
UML offers a framework for modeling systems and can be utilized for a variety of different purposes, such as analysis, or the design, implementation, documentation, and even testing of systems.
Based on object-oriented programming (OOP), UML features a variety of symbols that can be used to describe any type of system.
Depending on which aspects of a process are being studied, sequential, flow, or state charts and diagrams can be used.
Sequential UML diagrams show how a process occurs, step by step. They're useful for determining whether a process includes all necessary elements and if employees are following them in the correct order.
Flow charts indicate the different states a process moves through, as well as which actions are required to change its state from one to the next.
These can also help identify errors or mistakes in the process and determine why a process doesn't work as intended.
State machine diagrams visualize the states an object can be in and the conditions that are necessary for it to reach a certain state within a given amount of time.
This kind of diagram can help understand complex processes as well as identify errors or mistakes.
Event-Driven Process Chains (EPC)
Event-driven process chains (EPCs) are an extremely popular process modeling method.
As their name suggests, they're based on events that occur within a specific order. These events can be helpful in better understanding and visualizing complex processes.
EPCs are comprised of several linked activities. Each event sparks an activity in reaction. The order in which activities within an EPC occur is dependent upon which events are triggered.
Events can be manually or automatically triggered. An example of a manually triggered event would be clicking on a button or sending a form.
Automatically-triggered events might be when a particular date is reached, or a certain message is received.
In an EPC, activities are depicted as symbols and connected with arrows. These indicate which activities occur in response to which events and make it easy to understand interrelationships.
EPCs are typically used in project management, as well as business project management applications.
They're useful in other areas too though, such as software development, particularly when it comes to planning product processes or executing business ones.
In contrast to the other modeling methods, like BPMN, EPCs aren't well-suited for analyzing and optimizing business processes.
Process Modeling in Practice
Process models help to understand and visualize complex business workflows. They're also great for improving and developing new processes.
To make sure that you get the most out of your first experience with process models, here are a few suggestions.
Tips
Before you start to create process models, consider the following:
Specify a goal/target for your model
Before you begin process modeling, know what your goals and expectations are.
Which improvements would you like to achieve through process modeling? Should the models serve to optimize existing processes or develop new ones? Which areas of your company will be impacted by the modeling?
Answer these questions in advance to avoid misunderstandings and make success more likely.
Choose the right method
There are many different process modeling methods. Picking the right one depends entirely on what your goals are. If you would like to optimize an existing process, flow charts or BPMN can be helpful.
Read up on the various methods, their strengths and weaknesses, and determine which is the most relevant to your goals.
Assemble your team
Successful project modeling requires an effective and reliable team.This should consist of process modeling experts, as well as employees who are familiar with the processes under study. In this way, modeling errors can be avoided, and the results can be as relevant as possible.
Gather all necessary information
Before you begin modeling, you'll need plenty of relevant information, such as data about current processes, as well as feedback from employees and customers who interact with the processes.
The more information you have, the better you can understand and more effectively model the process.
Set realistic goals
Modeling is helpful, but it isn't a magic potion. Set realistic goals and expectations to avoid disappointment with the final results.Communicate effectively
Good and open communication is decisive for most business projects and process modeling is certainly among them.Make sure that all stakeholders are kept up to date on the project and address any questions or concerns as quickly as possible. In this way, you'll avoid misunderstandings.
Be consistent
If you start to model a process, you should continue to develop and improve it over time as well. This doesn't mean that you need to get a perfect model the first time.Rather, regularly check your models and adjust them accordingly. Only in this way can you be certain that your processes are accurately reflected in the model.
What Kinds of Project Modeling Software Are Available?
If you'd like to begin process modeling, you'll need specialized software. This makes it possible to create, edit, and analyze your processes. The most important features of process modeling software are the ability to:
Create process charts
Analyze processes
Manage process data
Import and export process charts
There are a range of different process modeling tools and software solutions. Most are commercial, and businesses need to pay to use them. There are a few free tools, however.
Some of the most well-known process modeling tools include:
Finding the right tool depends entirely on what your needs and preferences are.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Process Modeling
Process models are useful and versatile tools for optimizing business processes. However, like all methods, process modeling has both strengths and weaknesses:
Advantages
Allows for complex processes to be effectively visualized and communicated
Helps to better understand and analyze processes
Can be used to develop scenarios and assess the potential impacts and effects of changes
Facilitates communication among all project members, since everyone works on the same model
Errors or mistakes can be easily recognized and corrected
Supports project planning and execution since it provides a clear picture of the process's goal
Can help to optimize existing processes and develop new ones
Disadvantages
Time-intensive, especially with complex systems
Lots of preparation and planning needed
Can be difficult to incorporate changes or new features into existing models
Not all processes can be easily modeled
Process models can have errors if aspects are overlooked or misunderstood
Complex processes might remain difficult to understand
Conclusion
Process models come in handy for visualizing business processes. With them, organizations can graphically represent complex processes and make them easier for stakeholders to understand and optimize.
However, when choosing a model, it's important to consider which is best for your needs. There are many process modeling tools available, both free and premium.
Success depends not just upon which software and model you select, but also that you make the right preparations: Ask the right questions and take time to visualize complicated business processes to get the most out of this method.