Anonymity is a scarce commodity online. This is primarily because your individual IP address offers insight into your identity, location, and Internet Service Provider (ISP). Whenever you visit a website, it receives your IP address, unless you use an intermediary, like a proxy server.
Proxy servers are web servers that operate between your device and the Internet. They forward your requests to the websites you want to visit and then send the resources back to you. Accordingly, they ensure that there's never a direct link between you and a website since they don't receive your IP address or information about your ISP or location.
What Are Proxy Servers Good For?
Proxy servers can have many uses for individuals, organizations, and businesses. These include:
Anonymous surfing
Since proxy servers hide your IP address, others don't get any clues about your identity. Using them provides a certain degree of anonymity.Circumvent geo-restrictions
By changing the proxy server you connect to, you can alter your virtual location. This makes it possible to fool platforms like Netflix or BBC iPlayer and access geo-blocked content. In this way, you can also beat digital censorship, like the Great Firewall of China.Filter content
Proxy servers are especially popular on corporate or organizational networks for blocking certain kinds of requests. Should you not want users to have access to specific websites or engage in filesharing, you can prevent both with a proxy server.Enhance speed
With proxy servers, you can locally save copies of transferred data, meaning that websites you visit frequently will load faster. Instead of transferring data every time you access a website, it can be temporarily stored in your cache (caching).Burden-sharing
Websites can also rely on proxy servers as a sort of digital doorman, capable of reallocating traffic in order to minimize resource usage and maintain stability.
As can be seen from the above, proxy servers definitely have a number of practical uses. So how do they work?
How Does a Proxy Server Work?
Whenever you visit a website, let's say with your computer's browser, your device sends a request to that website's target server. Among other things, this request includes your IP address. The target server uses this to see where the request originated from and where the reply needs to be sent.
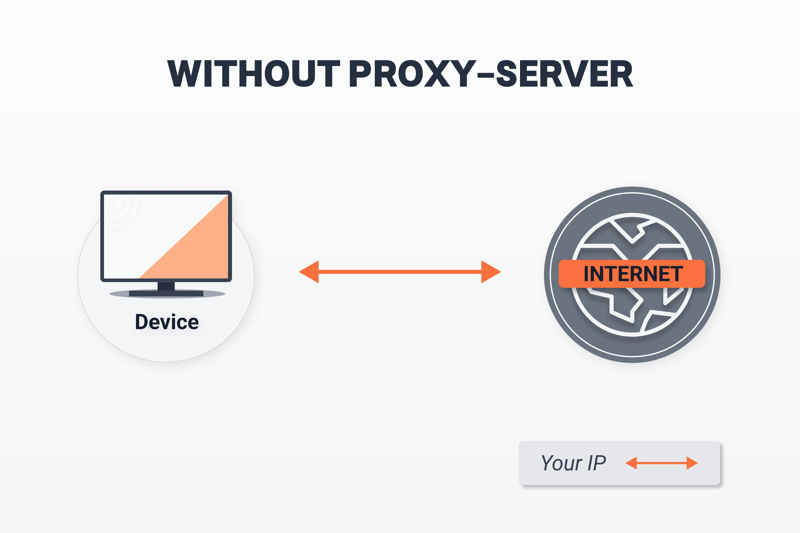
Without a proxy server, your Internet requests are sent directly to the website you intend to visit.
Should you use a proxy server, it acts as a middleman between you and the target server. Once you've input a URL and sent your request, it winds up at the proxy server. From here, it's forwarded to the target server of the website you want to visit, but with the proxy server's IP address rather than your own. You remain anonymous.
The target server's reply is sent back to the proxy server (and then to you), preventing any direct contact between you and the network.
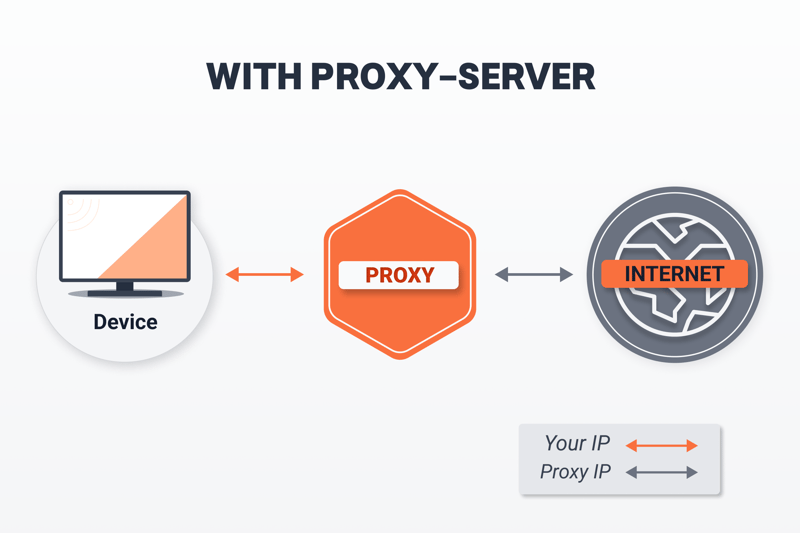
Proxy servers operate in between you and the Internet, hiding your IP address.
All proxy servers operate on this general principle, however, different types of proxies have varied uses and applications.
What Types of Proxy Servers Are There?
Not all proxies are created equal: Proxy servers can be grouped into numerous categories, based on how much anonymity they provide or the connection's properties. Since there is considerable overlap between these, it's common to distinguish between three main types of proxy servers:
Forward and reverse proxy servers:
Forward proxies are classic proxy servers that receive requests from the client (such as your browser) and route them to the target server. Reverse proxies operate in the opposite fashion, receiving requests from a target server. This is useful when a site operator wants to check incoming requests for security reasons or to allocate them to different servers (burden-sharing).Transparent and anonymous proxy servers:
Anonymous proxy servers hide the client's IP address, allowing users to go around content restrictions or firewalls. A further distinction exists between "regular" anonymous servers that identify themselves as proxy servers, and "high anonymity" proxy servers, which cannot be identified as such.
Transparent proxy servers are the opposite, disguising neither themselves nor the IP address of their clients. These are frequently used by businesses or schools for content filtering.HTTP(S) and SOCKS proxy servers: HTTP proxy servers are specifically configured to forward HTTP requests, limiting their applicability to web content. HTTPS proxies encrypt traffic by adding the HTTPS protocol. SOCKS proxy servers are more flexible and forward all kinds of traffic, meaning that they can also be used for torrents or email clients.
How to Use a Proxy Server?
There are several different ways to use a proxy, each of which varies in terms of ease, flexibility, and security.
Web Proxy
A web proxy is the easiest way to use a proxy server. You won't have to configure anything but simply navigate to the service's website. Once there, input the URL you'd like to visit, select a server location (if offered), and eventually, modify the cookie or script options. After that, the web proxy will forward your request to the proxy server you've selected and direct you to the website.
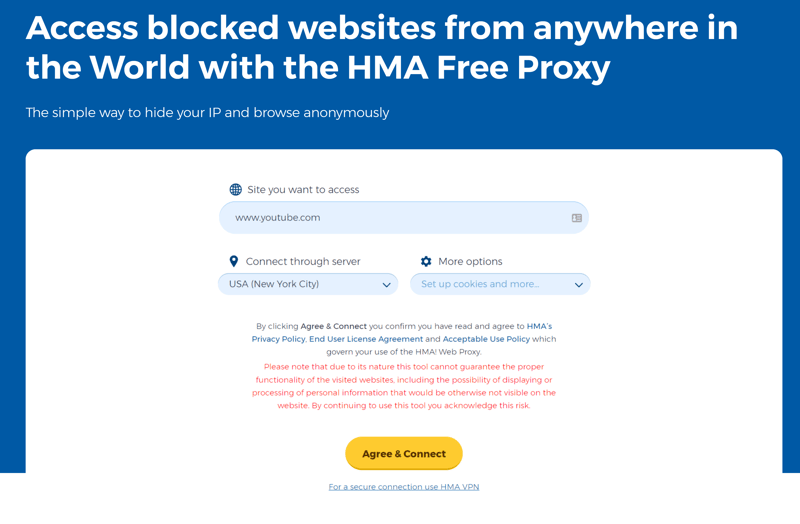
With a web proxy, you can establish a proxy connection in a few clicks.
The advantage of using a web proxy is its simplicity: You don't have to configure anything and can take advantage of them so long as you have a browser and an Internet connection. Of course, they also suffer from some disadvantages: To start, they usually aren't very fast or reliable, making them poorly suited for video streaming. Compounding this, most of the time they only support web traffic.
In our web proxy article, we detail everything you need to know about these browser-based tools.
Web Proxy Browser Extension
In case navigating to the web proxy's website each time you want a proxy connection doesn't sound appealing to you, a browser extension might be worth considering. For example, HideMyAss offers just such a tool at no cost. At its core, this is a basic web proxy solution that differs from the above method only in negating the need to visit the service's website.
With a proxy browser extension, you won't need to visit the service's website every time you want to create a proxy connection.
If you're looking for greater flexibility and enhanced performance, you can also manually configure a proxy in your browser. Our guides for Google Chrome (Windows) and Mozilla Firefox walk you through just how to do this.
Manual Configuration on Your Operating System
If you'd like to use a proxy server for your entire Internet connection, you'll need to set this up at the operating system level. Windows offers two basic options exist for this when navigating to Settings > Network and internet > Proxy:
You can run an automatic setup script from your university or organization, or manually configure the proxy server. For this, you'll need the IP address of a proxy server, which you can take from our list of free proxies, or rent one for a fee. Free servers are often slow and/or unreliable.
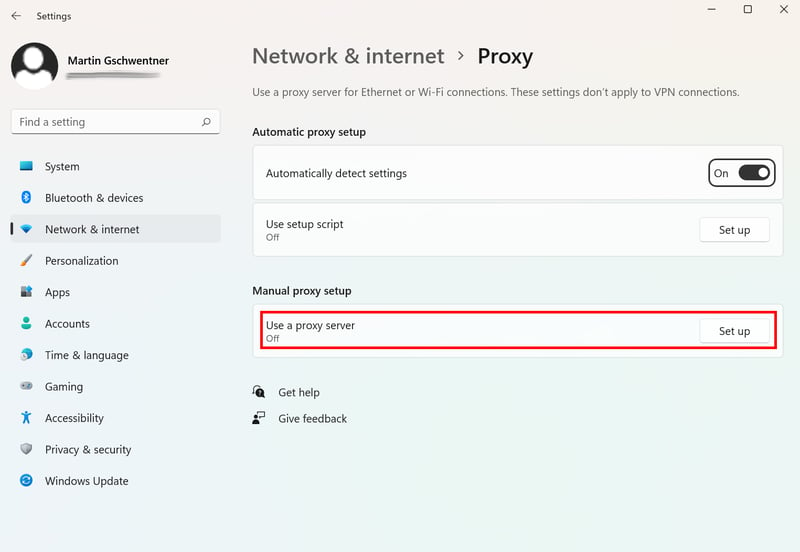
One advantage of configuring a proxy on your operating system is that you can use it for all of your Internet traffic.
We've created a step-by-step guide for how to setup a proxy server on your operating system.
What Are the Disadvantages of a Proxy Server?
Proxy servers are useful, however, in comparison to other solutions, they do have a few disadvantages:
Speed and reliability
Free proxy servers are often slow and unreliable. For that reason, you might have to frequently change the server you've connected to.No encryption
Proxy servers provide some anonymity, however, they usually don't encrypt your connection. There are better ways to conceal and protect your digital identity.Security risks (operator)
Most of the time those operating proxy servers are unknown, especially when the services are free. Accordingly, there is some danger of a shady individual or group monitoring your activities or manipulating HTML.Limited uses
Depending on the type of proxy server, the resulting connection can be restricted to certain kinds of traffic, like HTTP.User-friendliness
Free web proxies are easy to use, which is great, however, you'll only tap into the true potential offered by proxy servers when you can manually configure and/or pay for them. This shouldn't pose too much of a hurdle for beginners but is more complicated than other solutions.
Alternatives to Proxy Servers
The readiest alternative to proxy servers is a VPN. These virtual private networks also serve as intermediaries between you and the Internet, hide your identity, and make it possible to change your virtual location with the click of a mouse. Despite these similarities, there are a number of key differences: VPNs offer far more security since they don't just conceal your IP address, but also your complete Internet traffic.
Below, we've summarized the key differences between a VPN and proxy server:
Proxy server | VPN | |
|---|---|---|
Encryption | None (generally) | Entire connection |
Costs | Most often free (with limitations) | Most often premium, but also free (with limitations) |
Usage | Manual setup needed (except web proxies and browser extensions) | User-friendly apps |
Speed | Theoretically faster, but depends entirely on the proxy server | Loss of speed owing to encryption, however, connections are more stable |
Reliability | Varies from proxy server to proxy server | Generally high |
Owing to their encryption standards, the stability and reliability of their connections, and their ease of use, VPNs offer an attractive alternative to proxy servers. You should keep in mind that good VPNs without speed or bandwidth limits are typically premium (there are some exceptions, however).
There are plenty of VPNs to choose from. In our EXPERTE.com VPN comparison, we assessed 27 of the leading solutions, crowning a winner:
EXPERTE.com's Top VPN: NordVPN

NordVPN combines user-friendliness with excellent speeds (as determined by our VPN speed test) and a sizable server network. The Panama-based provider's security standards are high as well: They promise not to save logs and back up their claims with regular third-party audits.
EXPERTE.com's winner, NordVPN, excelled thanks to its speed, features, and security.
All important VPN features (including split tunneling) are offered. You'll also be able to take advantage of "specialty servers", such as those optimized for P2P platforms or Onion Over VPN. The latter offers enhanced anonymity by connecting to Tor network.
Since NordVPN is priced competitively, we have no problems voicing our opinion that it offers the best VPN package on the market.
Conclusion
Proxy servers operate between a client (like your browser) and the Internet. Since they conceal your IP address and location, they're great for getting around geo-restrictions. At the same time, they have a number of other features that might interest individuals and organizations.
While free, don't count on them to encrypt your Internet connection, or be particularly reliable. For these reasons, VPNs are a popular, albeit premium alternative: They work at the operating system level, encrypt your entire Internet traffic, and are stable.
If you'd like to manually set up a proxy server, you can select a free proxy IP from our regularly updated EXPERTE.com list. On the other hand, if you're interested in exploring VPNs, a good place to start would be our exhaustive comparison of 27 leading providers.
FAQs
A proxy server is an intermediary between a client and a target website. It receives requests from a browser (client) and forwards them to a web server (target), eliminating any direct contact between the two. In this way, information such as the sending device's IP address remains unknown to the web server.
Proxy servers have a number of uses, both for individuals as well as for organizations or businesses. They're practical for circumventing geo-restrictions, such as with streaming platforms like Netflix. Businesses and institutions can use them to filter content or make their websites more stable by burden-sharing.
To take advantage of all of the benefits proxy servers offer, you'll need to configure them at the operating system level. On Windows, head to Settings > Network and internet > Proxy. We've created a step-by-step guide, that shows just how to do this. Alternatively, you can use web proxies to create a proxy connection directly in your browser for specific websites.