Do you worry about your online privacy, but not enough to pay for a premium VPN? Proxy servers offer a free and efficient alternative that provides extra digital anonymity. They hide information that could identify you, like your IP address, and also help to bypass country or region restrictions.
Alongside the more well-known HTTP proxies, there are also SOCKS proxies, which stand out owing to their connection speed. In this article, we'll let you know about some of the other advantages SOCKS proxies have, as well as their disadvantages.
SOCKS Proxies: How They Work
A proxy acts as an intermediary between a user that wants to connect to a website or net-based application, and the server where that website or service is hosted.
Among other things, surfing on a proxy connection enhances your privacy, since it makes your IP address invisible to the website or service you're attempting to access. This also allows you to circumvent censorship and geoblocking and makes otherwise blocked websites or content available. A proxy server operates as an intermediary server between your computer or device and the target server.
Most of the time, when people talk about proxies, they mean those that use the HTTP protocol. A second, less well-known type of proxy server uses the SOCKS protocol.
SOCKS is an abbreviation of socket secure, a type of session-layer (OSI Layer 5) protocol. This regulates communication and connections between two network participants, like a client and a server. It's possible to send HTTP as well as POP and SMTP requests with the SOCKS protocol. Many email servers use these two protocols to exchange data.
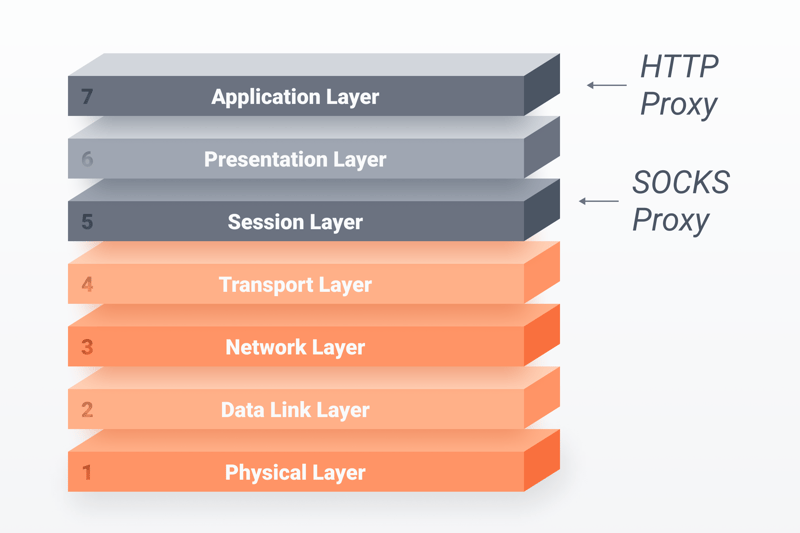
SOCKS proxies work at one of the lower layers of the OSI model, and support more connection types than HTTP proxies.
Most of the time, the SOCKS protocol is used to establish connections between a computer behind a firewall and a server. Such firewalls are common in corporate networks or Intranets. Since a SOCKS proxy filters and forwards requests, it protects the computer.
The original variant, SOCKS4, supports neither individual user authentication nor UDP requests. This puts it at a disadvantage, since UDP, an Internet protocol, is often used for streaming and DNS requests. Authentications are also essential to commercial providers. For this reason, the developers of SOCKS overhauled their protocol and introduced SOCKS5, which offers both UDP connections as well as authentications.
SOCKS vs. HTTP Proxies: The Differences
When opening a website in Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox, you'll connect to the target server using the HTTP protocol. This occurs on the highest layer of the OSI model (Layer 7) and facilitates communication between a browser and a server. HTTP proxies were primarily designed to support such browser-based HTTP connections.
As a result, there are several differences between HTTP and SOCKS proxies:
Supported protocols – You'll be able to surf the Internet without issues on an HTTP proxy, however, filesharing with P2P applications won't work, since these rely on other protocols. Accordingly, SOCKS proxies are more flexible and facilitate communication to a greater extent thanks to the larger number of protocols they support.
Privacy and data protection – HTTP proxies occupy the highest layer of the OSI model and are capable of reading any data they receive. SOCKS proxies don't possess these capabilities, since they're on a different OSI layer. However, they do provide enhanced data security. On the other hand, because they're unable to "read" this data, they can't filter out unwanted, infected data packets, like malware.
Security – When discussing an HTTPS proxy (in contrast to an HTTP proxy), connections between the client (your computer) and the proxy are encrypted. Third parties can only see that you've sent a proxy request, but won't be able to capture any data. In contrast, SOCKS proxies do not encrypt client-proxy connections.
Speed – A proxy server's speed depends on whether you select a private or public server. This makes it difficult to compare the performance of both proxy types. Generally speaking, SOCKS proxies are slightly faster, since they use a simple protocol.
Compatibility – All applications that support HTTP allow HTTP proxies, making them suitable for nearly all operating systems and programs. With SOCKS, compatibility isn't as far-reaching. However, you can still use SOCKS4 or SOCKS5 by installing Proxifier. This program allows a proxy connection to be established, even if you haven't installed the original application.
Ports – HTTPS proxys use ports 80, 8080, or 3128. This isn't set in stone though, and you can configure them to utilize other ports if desired. With SOCKS servers, the default port is 1080, but again, you can change this if you want.
VPN | HTTP Proxy | SOCKS Proxy | |
|---|---|---|---|
Encryption between client and intermediary server (proxy or VPN) | Yes | Some | No |
Hides IP address | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Circumvents geoblocking and censorship | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Protects against malware | No | Yes | No |
Speed | Very high | Varies from high to low (dedicated, semi-dedicated, or public) | High |
SOCKS Proxy List: Free SOCKS Proxies
Our constantly updated list provides a guide to free proxy servers around the world. Entries can be filtered by proxy type, location, and reliability. The last of these details how often a successful connection with the proxy was established. We also note when the last check was made, as well as the IP address and port number.
Should you be unable to find a suitable free proxy, just as with HTTP proxies, there exist premium providers that sell access to dedicated proxy servers.
There are paid services that offer premium access to SOCKS proxies.
Private proxies offer the advantage of being more exclusive, meaning that fewer users share the same connection. This makes the data transfer rate considerably higher than on public servers. Beyond that, customers can often select from multiple server locations and change servers in order to get around geoblocking or other regional restrictions.
Configure a SOCKS Proxy
If you'd like to use a SOCKS proxy to connect to the Internet in the future, you'll need to set one up on your operating system. This requires inputting the IP address and port number, regardless of whether you're using macOS, Windows, or a smartphone. Be sure to check out our step-by-step guide to see how exactly to proceed depending on your device and operating system.
Conclusion
SOCKS proxies offer a useful alternative to their more popular HTTP counterparts. In contrast to the latter, SOCKS proxies can be used with email clients, P2P software, and other applications. Still, there's a trade-off, as SOCKS proxies generally don't encrypt data by default.
Determining which type of proxy is best for you depends on your needs and what you intend to use it for. Should you primarily want a proxy to surf in your browser and protect against malware, HTTP proxies are a good option. However, if you'd like to quickly stream content from abroad that would otherwise be inaccessible owing to geoblocking, we recommend going with a SOCKS proxy.
FAQs
SOCKS proxies are proxy servers that act as an intermediary between a client and a server and use the SOCKS protocol. Should the client (your computer, for example) send a request to a server, its IP address will remain concealed. The server you've sent a request to will only see the IP address of the SOCKS server you used.
SOCKS proxies operate lower on the OSI model than HTTP proxies (Layer 5, as opposed to Layer 7). For this reason, and since they're generic, they support more protocols including POP3 (email), UDP (DNS servers), and SMTP. HTTP proxies, on the other hand, don't just support anonymous surfing and getting around geoblocking, but unlike SOCKS proxies, also encrypt data.
Our list of free proxy servers is regularly updated and provides information about their reliability. The list allows you to specify whether you'd only like to see SOCKS proxies.
SOCKS5 is the newer version of the SOCKS protocol. Unlike its predecessor, SOCKS5 is compatible with UDP requests and supports authentication. This allows commercial providers, for example, to sell exclusive access to dedicated SOCKS proxy servers.